Introduction to Biosimilars
What are Biosimilars?
A biosimilar is a type of biologic drug that are highly similar to an already approved reference biologic. These drugs are developed to have no meaningful differences in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality when compared to the reference biologic [1]. Biosimilars have the potential to offer significant cost savings compared to their reference biologics, making them important contributors to reducing healthcare costs. They are designed to have the same mechanism of action as the reference biologic, using the same manufacturing process that involves cell cultures and living cells. Biosimilars go through a rigorous regulatory approval process to demonstrate their similarity to the reference biologic and are expected to provide the same clinical outcomes [2]. They have the potential to increase access to high-cost biological products and provide lower-cost alternatives for patients, healthcare systems, and payers. The market competition between biosimilars and their reference biologics can drive down prices and create a more affordable and sustainable healthcare industry.
Benefits of Biosimilars
Biosimilars offer several benefits compared to their reference biologic drugs. One of the main advantages is the potential for significant cost savings in the health care industry. Biosimilars can be priced lower than their biologic counterparts, providing a more affordable treatment option for patients and reducing overall health care costs. Estimates of potential cost savings with implementation of biosimilars can range up to approximately $40B.
In addition to cost savings, biosimilars also increase access to treatment. With lower prices, more patients can afford these medications, improving their access to much-needed therapies. This expanded access can have a substantial impact on patient care, particularly for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis where biologics have demonstrated efficacy.
Another benefit of biosimilars is the increased market competition they foster. As more biosimilars enter the market, they create competition for the reference biologics. This competition can lead to further price reductions and incentivize innovation within the industry, ultimately benefiting patients.
Overall, biosimilars present a promising opportunity for the healthcare industry. With their potential for lower costs, increased access to treatment, and enhanced market competition, biosimilars have the potential to improve patient care and contribute to more sustainable healthcare systems.
Health Plan Savings from Biosimilars
Healthcare institutions can leverage biosimilars to generate cost savings by incorporating them into their formulary and treatment plans. By strategically selecting biosimilars over higher-priced biologic drugs, health plans can achieve considerable cost reductions. Biosimilars offer a comparable therapeutic effect to their reference biologics at a lower average sales price, providing a cost-effective alternative without compromising patient care.
To maximize the benefits of biosimilar savings, health care institutions can implement several strategies. First, they can negotiate favorable contracts with biosimilar manufacturers to secure competitive pricing. Second, by encouraging widespread adoption and utilization of biosimilars, health plans can drive market competition, resulting in further price reductions.
Additionally, health care institutions can implement biosimilar substitution policies, promoting the interchangeability of biosimilars with their reference biologics. This ensures seamless transitions for patients while generating cost savings from biosimilar utilization. An example of an expensive originator drug is Humira typically used for a variety of autoimmune conditions including Crohn's Disease, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Psoriatic Arthritis, and more [3]. Several biosimilars to Humira have or will be entering the market at lower price points.
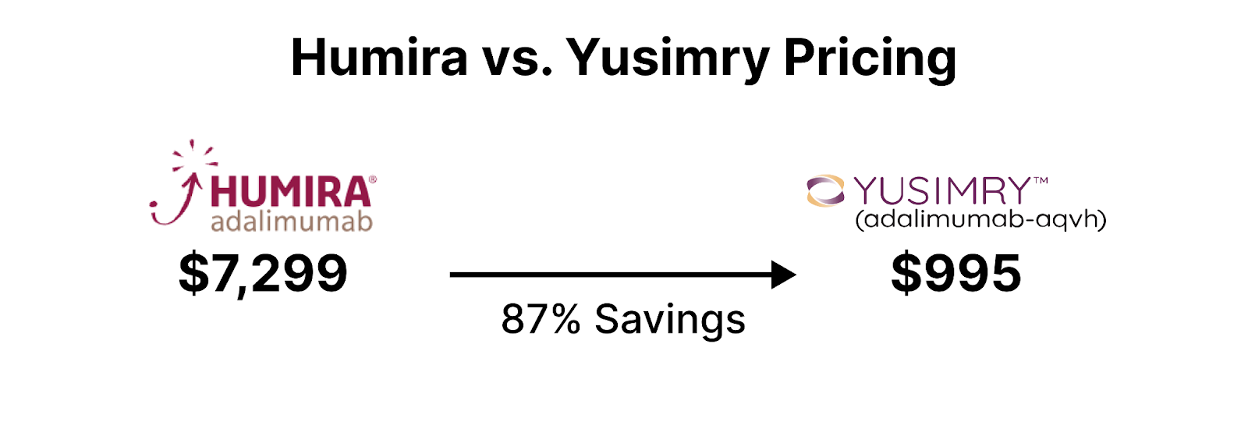
In conclusion, biosimilars present an opportunity for health plan savings in the healthcare system. By strategically incorporating biosimilars into formularies, negotiating favorable contracts, and promoting widespread adoption, healthcare institutions can effectively leverage biosimilars to achieve substantial cost savings while maintaining high-quality patient care.
Generic and Biologic Drugs: Meaningful Differences?
Generic and biologic drugs are two distinct categories of medications, each with their own unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between them is crucial in maximizing patient care and controlling healthcare costs.
Generic drugs are essentially identical copies of brand-name drugs. They contain the same active ingredients and are available once the patent protection of the brand-name drug expires. This allows for cost savings as generic versions usually come at a lower price point. However, generic drugs are typically small molecular compounds and are manufactured through a well-defined and relatively simple process, making them easier to replicate.
On the other hand, biologic drugs are complex medications derived from living cells or organisms. They consist of large, structurally complex molecules, often proteins or monoclonal antibodies, and are developed through a multi-step manufacturing process. Due to this complexity, it is impossible to create exact copies of biologics. Instead, biosimilars are developed to be highly similar to the reference biologic drug, but not identical. The United States FDA has approved over 40 biosimilars, offering less expensive versions of advanced biologic medications.
Despite not being identical, biosimilars undergo rigorous testing to establish their safety, efficacy, and purity. While biosimilars may have minor differences in the manufacturing process, formulation, or inactive ingredients compared to the reference biologic, they have been proven to have no meaningful differences in terms of clinical effectiveness, safety, and quality.
The availability of biosimilars presents significant potential for controlling rising drug costs. By introducing competition to the market, biosimilars can lead to price reductions for both the reference biologic and the biosimilar itself. This not only benefits patients by providing access to more affordable treatment options, but also has the potential to alleviate the financial burden on healthcare systems and insurers.
In conclusion, while generic drugs and biosimilars both offer cost savings compared to their respective brand-name or reference counterparts, their differences lie in their complexity and the level of replication. Biosimilars, which are less expensive versions of advanced biologic medications, have the potential to play a vital role in controlling rising drug costs, fostering competition, and increasing access to high-quality patient care.
References
[2] “U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). "Review and Approval"
[3] humira.com. “How HUMIRA® (adalimumab) Treatment Works for RA”
[4] drugs.com “Humira Prices, Coupons and Patient Assistance Programs
